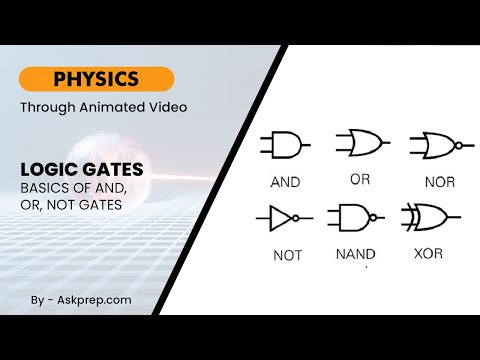
Logic gates are the building blocks of digital electronics. This blog breaks down the fundamental g…
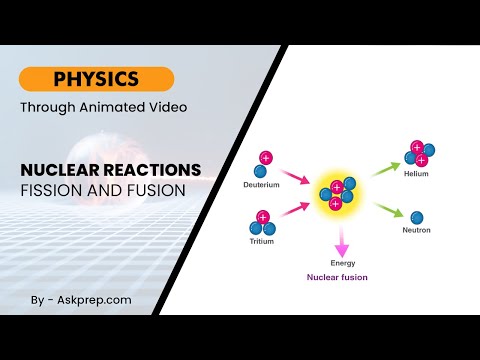
Read MoreNuclear reactions power stars and nuclear plants alike. This blog explores the two main types — fis…
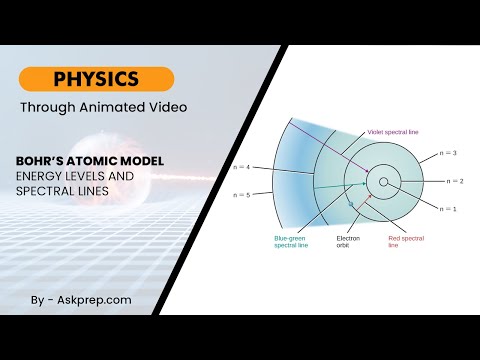
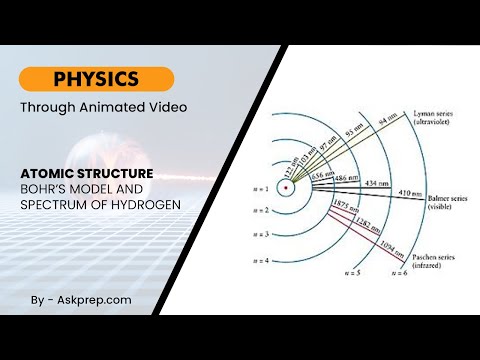
Read MoreBohr’s atomic model revolutionized our understanding of the atom by introducing fixed energy levels…
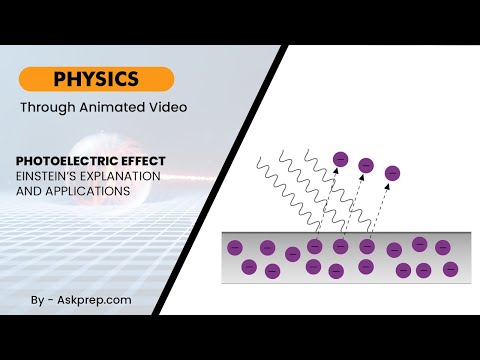
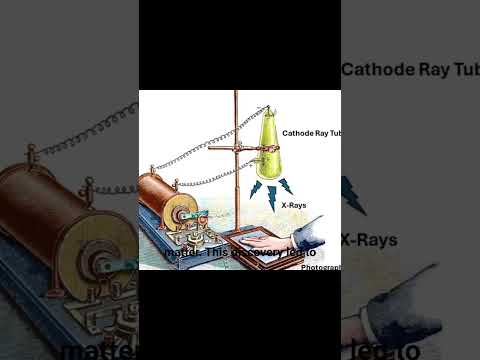
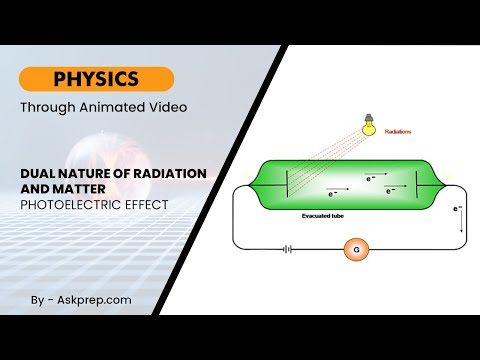
Read MoreThe photoelectric effect revealed a surprising link between light and electricity, shaking the foun…
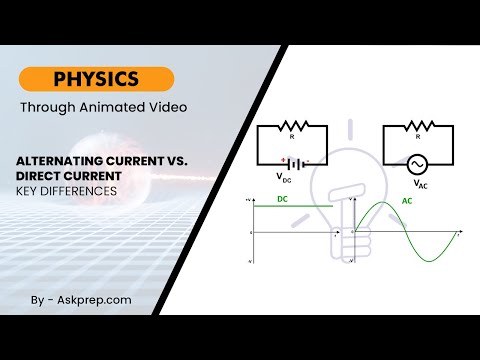
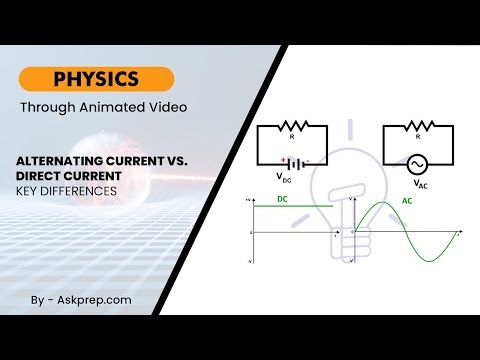
Read MoreAlternating current (AC) and direct current (DC) are two fundamental forms of electric power. This …
Read MoreElectric current not only powers devices—it also creates magnetic fields. This blog explores two ke…
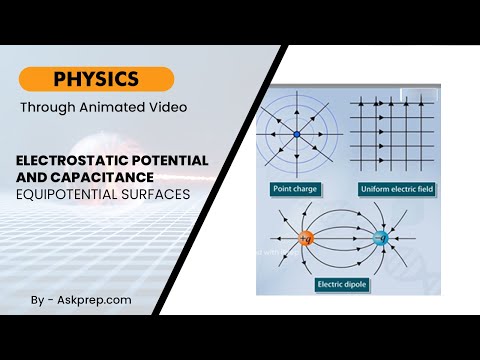
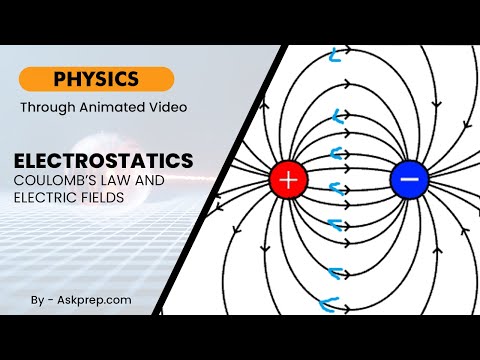
Read MoreElectrostatics is the study of electric charges at rest, and key to this is understanding electrost…
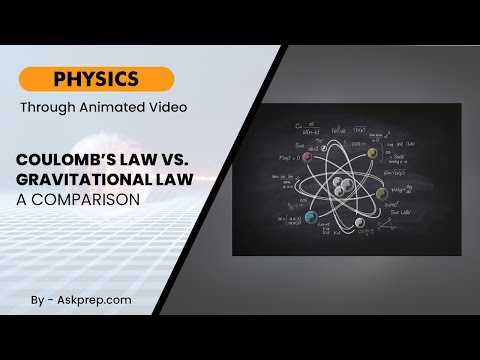
Read MoreCoulomb’s Law and Newton’s Law of Gravitation describe forces between two objects—but one deals wit…
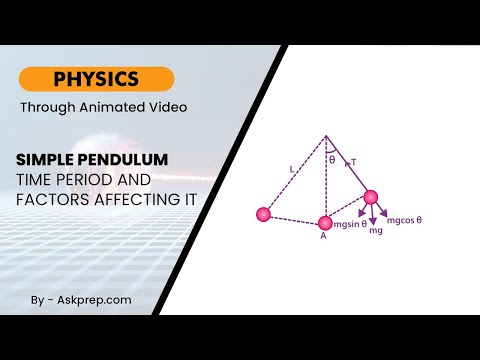
Read MoreA simple pendulum is one of the most fundamental systems in physics used to study periodic motion. …
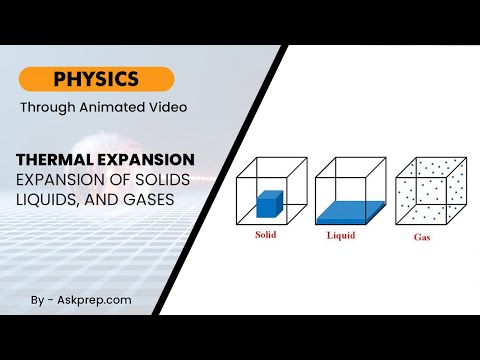
Read MoreWhen substances are heated, they expand. This blog explains the science of thermal expansion across…
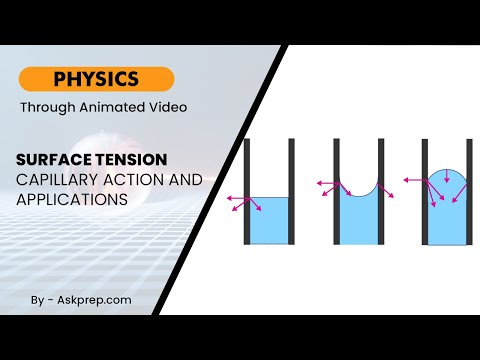
Read MoreWhy do water droplets form spheres? How does water climb up a paper towel or the roots of plants? T…
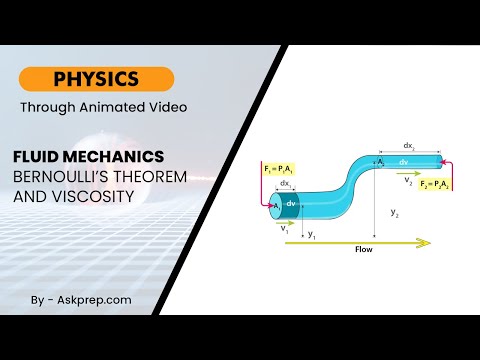
Read MoreFluid mechanics explores how liquids and gases move. In this post, we dive into Bernoulli’s Theorem…
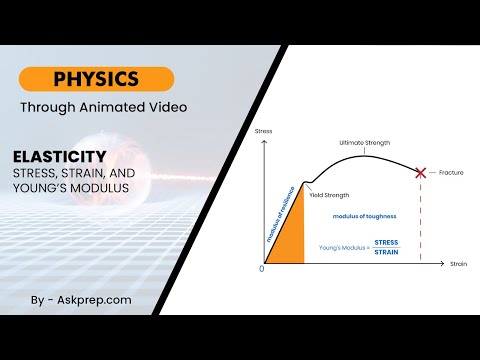
Read MoreElasticity describes how materials return to their original shape after being deformed. This blog b…
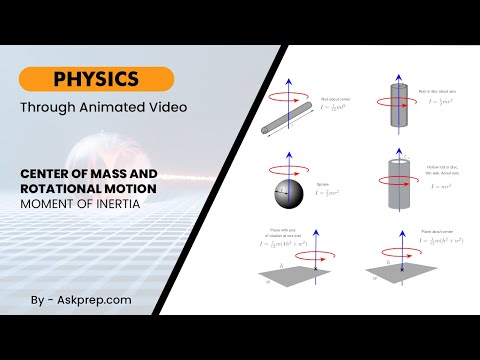
Read MoreThe concepts of center of mass and rotational motion help explain how objects move, balance, and sp…
Read MoreUnderstanding units and measurements is the foundation of all scientific study. In this blog, we ex…
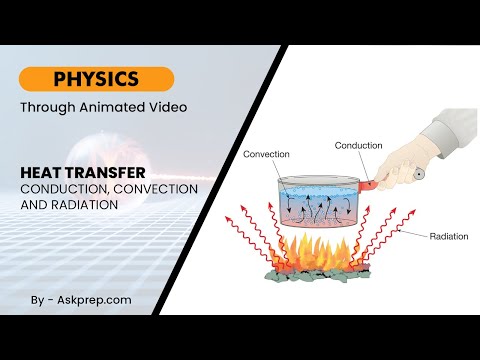
Read MoreHeat always flows from hotter to colder objects — but how it moves depends on the medium and mechan…
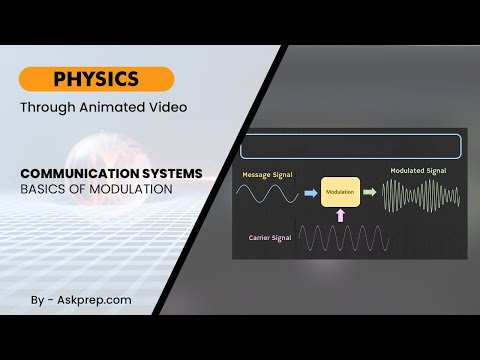
Read MoreCommunication systems are the backbone of modern technology, allowing us to transmit information ov…
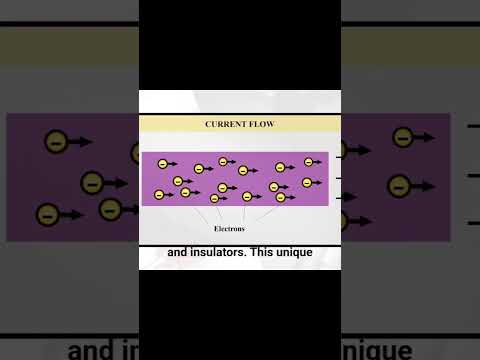
Read MoreElectricity powers nearly all modern devices, but not all materials conduct electricity in the same…
Read MoreSemiconductors are the foundation of modern electronics, with diodes and transistors playing crucia…
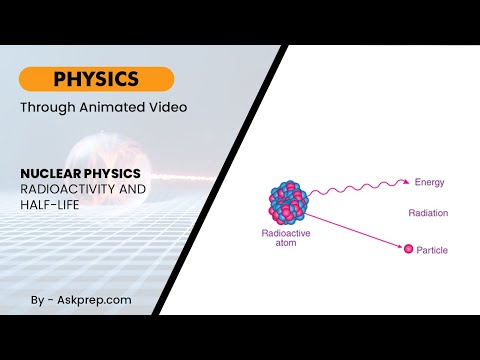
Read MoreRadioactivity is a fundamental concept in nuclear physics, playing a crucial role in various scient…
Read MoreRadioactivity is a fascinating and vital concept in nuclear physics, where unstable atomic nuclei r…
Read MoreBohr's atomic model revolutionized our understanding of atomic structure by introducing quantized e…
Read MoreThe concept of dual nature of radiation and matter reveals that both light and matter exhibit both …
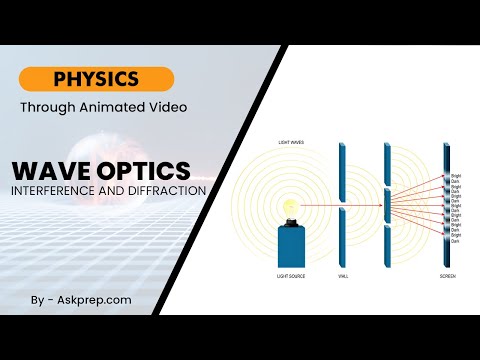
Read MoreWave optics deals with the behavior of light as a wave. Two of the most important phenomena in wave…
Read MoreRay optics, also known as geometrical optics, is a branch of optics that describes the behavior of …
Read MoreElectromagnetic waves are oscillations of electric and magnetic fields that travel through space, c…
Read MoreIn AC circuits, the interaction between inductors, capacitors, and resistors (LCR circuits) plays a…
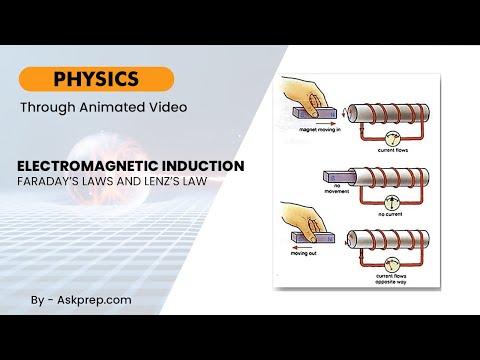
Read MoreElectromagnetic induction is the process of generating an electromotive force (EMF) or voltage in a…
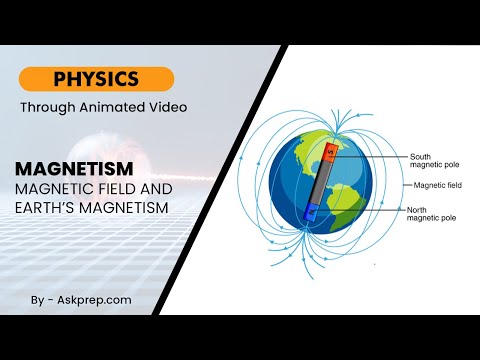
Read MoreMagnetism is a natural force caused by the motion of electric charges. It creates magnetic fields, …
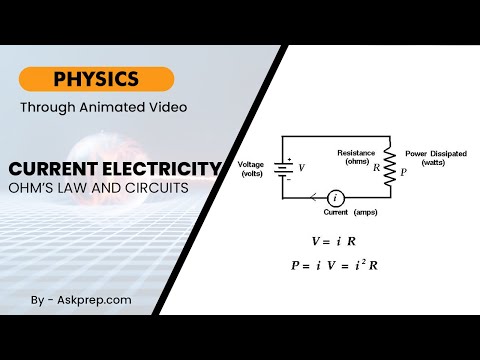
Read MoreCurrent electricity refers to the flow of electric charge through a conductor. It powers most of th…
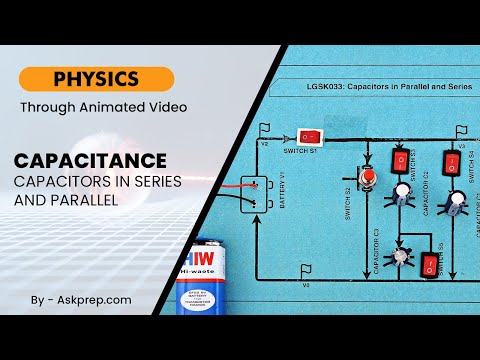
Read MoreCapacitance is the ability of a system to store electric charge. Capacitors are components designed…
Read MoreElectrostatics is the study of electric charges at rest and the forces they exert on each other. It…
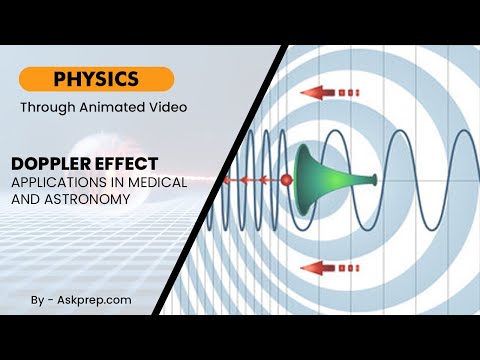
Read MoreThe Doppler Effect is a phenomenon where the frequency or wavelength of a wave changes based on the…
Read MoreWaves are fundamental phenomena observed throughout nature and science, from the gentle ripples on …
Read MoreOscillations are a fundamental concept in physics that describe repetitive motions or fluctuations …
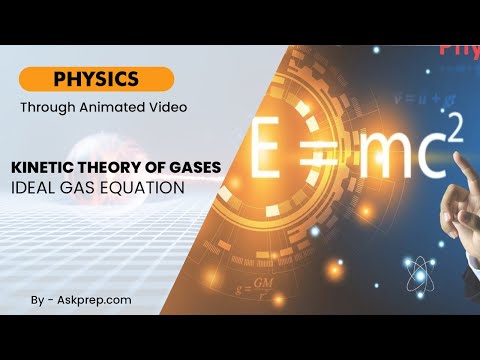
Read MoreThe Kinetic Theory of Gases provides a molecular-level understanding of gases and their behaviors. …
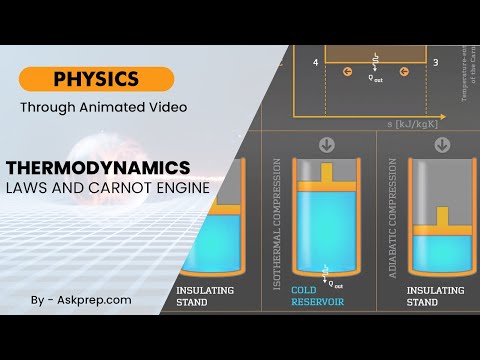
Read MoreThermodynamics is a branch of physics that deals with the study of energy, heat, and work and how t…
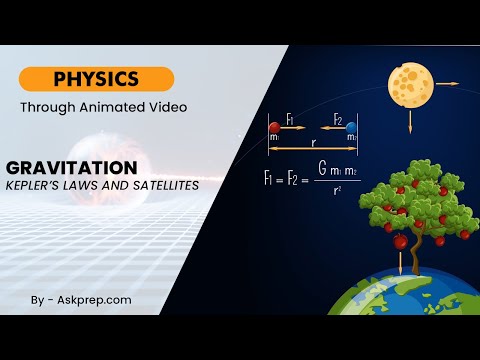
Read MoreGravitation is one of the fundamental forces of nature and governs the motion of celestial bodies. …
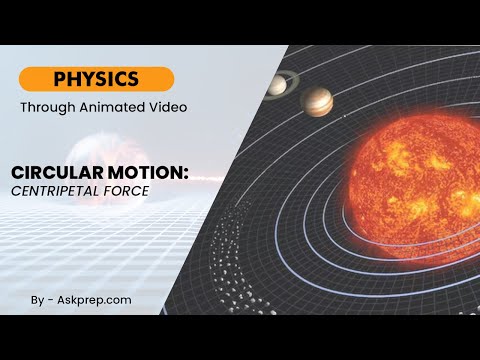
Read MoreCircular motion is a type of motion where an object moves along the circumference of a circle. This…
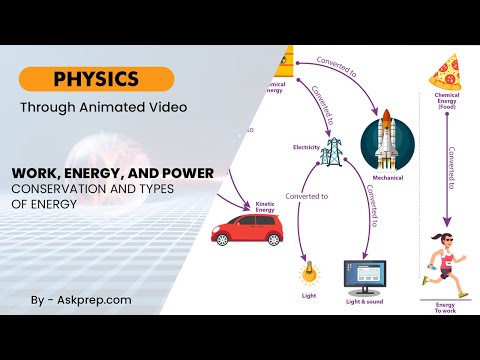
Read MoreWork, energy, and power are fundamental concepts in physics that explain how objects move and inter…
Read MoreKinematics is the branch of physics that deals with the description of motion. In classical mechani…
Read MoreNewton's Laws of Motion form the foundation of classical mechanics and describe how objects behave …
Read MoreChoose an option to continue: